MSP Global 2024 Review: A Journey from the Past to the Future
MSP Global 2024 took us on a thrilling journey through technology’s evolution, blending cutting-edge cloud innovations with the charm of PortAventura World.
MSP Global 2024 took us on a thrilling journey through technology’s evolution, blending cutting-edge cloud innovations with the charm of PortAventura World.
Explore how The Phoenix Project’s principles of automation and integration enhance cybersecurity through cloud-based IT solutions.
Discover how the 3-2-1 backup rule and cloud computing can transform your data strategy into an antifragile system that not only survives disruptions but grows stronger from them. Learn how LifeinCloud helps businesses thrive in uncertainty.
Explore how managed IT services can help your business thrive by allowing you to scale and innovate. Drawing lessons from “The Innovator’s Dilemma,” find out how outsourcing IT management can free up your time, save costs, and keep you competitive in a disruptive market.
The London MSP Summit 2024 highlighted the intersection of AI, cybersecurity, and business transformation. From embracing innovation to addressing challenges like talent shortages and regulatory compliance, the event showcased strategies that businesses can adopt to stay competitive in a rapidly changing technological landscape.
Attending MJ The Musical sparked a realization: authenticity in business isn’t just a buzzword – it’s the key to long-term success. Explore how LifeinCloud embodies this philosophy and why customers crave originality over imitation.
As we prepare for the London MSP Summit 2024, we’re ready to explore the latest trends and developments in managed IT services. Stay tuned for updates and insights from the event.
The image below offers a fascinating glimpse into the automation process, a journey that is fundamentally transforming the way we work.
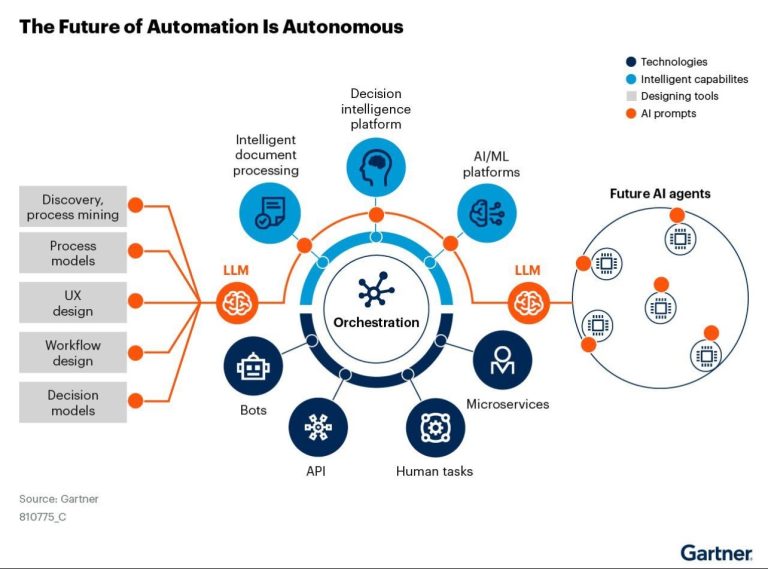
The journey depicted in the image is a map, not a destination. By understanding the stages of automation, leveraging the power of cloud computing, and learning from the past, we can ensure that automation empowers us to build a future of work that is both efficient and fulfilling.
Let’s see how we can achieve this with minimal impact on what defines human nature, particularly utility.
Automation has evolved significantly over the past few decades, moving from simple mechanization to advanced intelligent systems. The image titled “The Future of Automation Is Autonomous,” sourced from Gartner, provides a comprehensive overview of the components and processes involved in achieving autonomous automation. This article explores the various elements depicted in the diagram, shedding light on how businesses can leverage these technologies to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and foster innovation.
In discussing the transformative power of automation, it’s essential to draw parallels with historical moments that reshaped society and work, much like the advent of the Industrial Revolution. Books such as “The Fourth Industrial Revolution” by Klaus Schwab and “The Second Machine Age” by Erik Brynjolfsson and Andrew McAfee, offer profound insights into these shifts.
Core Elements of Automation
1.Discovery and Process Mining:
This initial step involves identifying and analyzing existing business processes. Process mining tools help uncover inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement by analyzing data from various sources. This foundational layer is crucial for understanding the current state of operations and setting the stage for automation.
“The Fourth Industrial Revolution” by Klaus Schwab gives a deeper understanding of how technological advancements historically disrupt and redefine industries. Schwab discusses how the digital revolution, much like the industrial revolution, necessitates a re-evaluation of existing processes and workflows. Process mining, in this context, is akin to the early stages of industrialization, where understanding the existing landscape was critical for implementing mechanization.
2. Process Models:
Once processes are identified, they are documented and modeled. Process models serve as blueprints for automation, detailing the workflow, tasks, and decision points involved. These models are essential for designing automation solutions that align with business objectives.
In the book “The Second Machine Age”, Brynjolfsson and McAfee highlight the significance of digital models and blueprints in enabling automation. They argue that “just as the steam engine and electricity freed labor from physical tasks, digital technologies are now freeing knowledge workers from cognitive tasks.” This resonates with the function of process models in modern automation, setting the stage for machines to take over complex decision-making tasks.
3. UX Design:
User Experience (UX) design focuses on creating intuitive and efficient interfaces for interacting with automated systems. Good UX design ensures that users can easily navigate and use the systems, enhancing productivity and user satisfaction.
The emphasis on UX design in automation parallels the user-centric approaches discussed in “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries. Just as Ries emphasizes the importance of feedback loops in product development, UX design in automation must continuously evolve based on user feedback to remain effective and relevant.
4. Workflow Design:
Workflow design involves structuring the sequence of tasks and activities to optimize efficiency. In an automated system, workflows are designed to minimize manual intervention, reduce errors, and accelerate task completion.
In the book “The Innovator’s Dilemma”, Clayton Christensen analyzes the business process innovation, emphasizing the need for companies to adapt their workflows to leverage disruptive technologies. He notes that “established companies often fail to capitalize on new technologies because they are not integrated into existing workflows.” This insight underscores the importance of proactive workflow design in adopting automation technologies.
5. Decision Models:
Decision models define the criteria and rules for automated decision-making. These models are essential for systems that need to make decisions based on data inputs, such as determining the next steps in a process or identifying exceptions.
Reflecting on “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman, decision models in automation mirror the interplay between the brain’s fast and slow thinking processes. Automation often takes over the “fast thinking” tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex, “slow thinking” decisions, thus enhancing overall efficiency and decision quality.
Intelligent Capabilities and Future Implications
As automation technology continues to evolve, it incorporates intelligent capabilities such as AI and machine learning, as discussed in “Superintelligence” by Nick Bostrom. Bostrom’s exploration of the potential of AI to surpass human intelligence highlights the critical role that these technologies will play in future automation.
The integration of AI and machine learning into automation, as depicted in the Gartner image, echoes Bostrom’s predictions about the transformative potential of superintelligent systems. These technologies enable businesses to automate not just routine tasks but also complex decision-making processes, pushing the boundaries of what is possible with automation.
In conclusion, the journey towards autonomous automation is akin to significant historical shifts in industry and society. By drawing from books such as “The Fourth Industrial Revolution”, “The Second Machine Age”, and “Superintelligence” we can better understand the transformative impact of automation technologies. As businesses continue to adopt and integrate these technologies, they must remain agile, innovative, and responsive to the ever-changing landscape of digital transformation. These insights not only enrich our understanding of automation but also prepare us for the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, businesses constantly face the decision of whether to migrate their operations from on-premises infrastructures to cloud computing environments. This decision is akin to the monumental shifts in industry and economy chronicled in history books such as “Guns, Germs, and Steel” by Jared Diamond. Just as those great decisions shaped the future of humankind, the choice to transition to the cloud can significantly impact the trajectory of a business. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding when it’s the right time to make this leap, the advantages and disadvantages of cloud migration, and the historical parallels that underscore its importance.
The Winds of Change: When to Embrace the Cloud:
Pros of Cloud Migration:
Nothing is 100% good or bad, so there are some disadvantages. However, these are not significant enough to outweigh the overall benefits. These drawbacks are more like occasional side effects, similar to those of a medical treatment. We are aware of the potential ‘blind spots’ and through our consultancy, we can greatly minimize their impact.
Cons of Cloud Migration:
Learning from Great Decisions:
In “Guns, Germs, and Steel,” Jared Diamond explores how the decisions to adopt agriculture, metallurgy, and other technological advancements transformed societies and economies. Similarly, the decision to migrate to the cloud represents a transformative step for modern businesses. Just as early societies weighed the benefits and risks of adopting new technologies, contemporary businesses must carefully consider the timing and implications of cloud migration.
Industrial Revolution: The shift from manual labor to mechanized production during the Industrial Revolution is analogous to moving from on-premises to cloud computing. Both transitions involve embracing new technologies to achieve greater efficiency and scalability.
Economic Shifts: The global economy’s move from agricultural to industrial and now to information-based paradigms reflects the ongoing evolution in business operations. Cloud computing is the latest frontier in this progression, offering new ways to leverage information and technology.
Cloud Computing: A Brief History and Evolution
The concept of cloud computing has roots that trace back several decades. Here’s a brief overview of its evolution:
The Path Forward – A Calculated Risk:
In the words of historian Yuval Noah Harari, “The most important thing is to be able to constantly learn and change.” As with the great decisions of the past, the choice to migrate to the cloud isn’t without risk. Yet, with careful planning, thorough research, and a willingness to adapt, the cloud can empower businesses to thrive in the digital age, much like the Industrial Revolution propelled those who embraced its innovations.
Determining the right time to migrate your business to the cloud involves assessing your current needs, future growth prospects, and the specific advantages and disadvantages of cloud solutions. By drawing parallels to historical decisions that shaped human progress, it becomes clear that embracing cloud computing can position your business for greater flexibility, efficiency, and resilience in the face of modern challenges. Just as the great decisions of the past forged new paths for societies, the decision to migrate to the cloud can pave the way for your business’s future success.
The NIS 2 Directive (Directive (EU) 2022/2555) aims to enhance cybersecurity across various sectors by imposing stringent cybersecurity requirements and incident management obligations. It mandates entities to implement risk analyses, IT security policies, incident handling procedures, and more to mitigate cybersecurity threats effectively. Moreover, the directive emphasizes reporting obligations for potential incidents and allows coordinated vulnerability disclosure.
For companies leveraging cloud computing and managed IT services, compliance with NIS 2 is crucial to ensure robust cybersecurity measures and incident response capabilities. By adhering to NIS 2, organizations can enhance their security posture, fortify supply chain security, improve network security, and strengthen access control measures.
Additionally, aligning with NIS 2 requirements can increase cybersecurity awareness, preparedness, and resilience against cyber threats, ultimately safeguarding critical infrastructure and services.
The key cybersecurity measures required by the NIS 2 Directive include:
Cloud computing solutions offer cybersecurity benefits by enabling antifragility, a concept from Nassim Taleb’s book “Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder.” Antifragility in cybersecurity involves systems improving in response to stressors, shocks, and attacks, unlike resilience which maintains the status quo. Cloud computing infrastructures can be designed to be antifragile, gaining from disorder and becoming more robust with each challenge.
Organizations can become antifragile in their cybersecurity measures by adopting the following strategies:
By adopting these strategies, organizations can move beyond mere resilience and become antifragile, actively learning and growing stronger from cybersecurity challenges.
Some basic protective measures for cybersecurity resilience include:
Some common cyber threats that organizations should be aware of include:
By applying antifragility principles to cybersecurity, organizations can enhance their ability to thrive in the face of cyber threats, moving beyond mere resilience to actively improving and evolving in the face of adversity.
![]()

You can also read some of this information in Romanian-published in the Club IT&C magazine.